Policy Innovation Labs – The new age of policymaking?
The development of innovative approaches to strengthen the provision of public goodsGoods where access to the good cannot be restricted and where use by one individual does not reduce availability to others. See also: Environmental Public Goods More is at the heart of Contracts2.0. The corresponding contractual solutions are co-designed by a diversity of stakeholders and practitioners in our regional Contracta formal, written agreement for a specified duration signed by (at least) two parties. In Contracts2.0, we acknowledge the existence of informal contracts but use formal contracts to focus the research. More Innovation Labs (CIL). To support the wider acceptance or the scaling up of these novel contracts, the Contracts2.0-Policy Innovation Labs (PIL) aim to lobby for the implementation of the innovative approaches into the respective policies on regional, national and EU-Level. The following article reveals how this is done in case of Contracts2.0 and what kind of general approaches are available to drive policy innovation.
The phrase “policy-making” can evoke a certain image in one’s mind. As something that is made by experts, technocrats and politicians, it is often associated with a rather hierarchical, strictly top-down process.
The remoteness of those who produce policies from those who will be affected by them is a major challenge for all levels of public policy — local, national and international.
So how does one bridge the gap between policy-makers and “policy-takers”, and make the process a bit less hierarchical? That’s where policy innovation comes in, as governments across the world try to experiment with the way in which policies are created, gradually moving away from the traditional ways of conjuring solutions behind closed ministerial doors. This novel approach to policy creation flips the entire process over, and the results have been quite promising.
Types of policy innovation
The realm of policy innovation abounds in methods and tools that all seek to resolve the same policy problem in various ways. Although the list of such methods is indeed very long, some of them have been successfully applied in practice to generate new policy ideas:
Policy experimentation for developing and testing policies has gained traction in recent years with increasing support for Randomised Control Trials (RCTs) by organisations such as the World Bank, and various initiatives to improve public service delivery and institutional efficiency. Chances are, if you’ve recently read about a major policy breakthrough, especially in the developing world, its effectiveness was probably established through RCTs.
Although experimentation in policymaking is often conflated with ‘innovation’, out-of-the-box thinking and trying out new or different ideas, in essence, it is a systematic process requiring rigorous evidence collection/generation and evaluation. It allows policymakers to assess the impact of potential policies by employing techniques such as piloting and prototyping. This enables them to gauge the cost-effectiveness of policy interventions to see if they require adjustment or even termination before they are rolled out or scaled up.
Despite the potential benefits, governments are often reluctant to innovate or veer too far from the status quo, fearing loss of investment or policy failure. However, with experimentation and evidence, there is immense potential for learning from failure as well and examining what does not work at the same time as trying to figure out what does. That is the model at the heart of the UK Cabinet Office’s What Works Network that has been replicated, amongst others, in Canada, the US, Finland, Colombia and the UAE. The pilot Accelerator Labs at UNDP are also experimenting with local innovations to achieve the Sustainable Development Goals.
Behavioural insights provide an inductive approach to policymaking research, borrowing from economics, psychology and cognitive science, and are often used to create incentives and ‘nudge’ people to follow an established policy. The behavioural approach is underpinned by experimentation and use of evidence related to typical patterns of behaviour in a cost-benefit context. This approach enables policymakers to create the environments to induce public to make decisions working towards the desired outcomes without changing any costs or benefits that they are faced with. While this kind of policy design can have ethical issues, nevertheless, it can be a useful tool for more effective policies.
While experimentation and behaviour-inducing policies are driven by evidence, strategic foresight is applied in cases where the future policy context is unclear and can only be modelled through tools such as trend analysis, horizon scanning and scenario planning. This allows policymakers to map plausible “futures” and situations that could arise as well as the corresponding challenges and opportunities. The Covid-19 pandemic has reinforced the necessity for such anticipatory measures, and the need to prepare and innovate for crises. This approach enables policymakers to ‘stress-test’ existing or potential policies and systems to anticipate risks and evaluate whether they can sustain future shocks.
In contrast to the technocratic (or top-down) types of policy creation involving exclusively expert knowledge and political will, there are also approaches that attempts to come up with new policies in a less hierarchical and more bottom-up way. There are many variations within this approach, but the gist remains the same: policies are to be made together (or co-designed) with those whom they will affect. This goes far beyond a mere consultative function, since direct and meaningful involvement of all parties is key.
Policy Innovation Labs (PIL)
One of such novel approaches to policymaking that uses co-design is the Policy Innovation Lab (PIL), which engages various stakeholders in an innovative co-creation of policies. Taking a holistic view of whatever problem is at hand, this approach brings together policymakers, scientists, community representatives and whoever is at least tangentially related to the particular context of the problem.
This multi-actor composition is designed to address the issues of ineffective policymaking and low levels of policy acceptance (i.e. popularity among those that it is designed to affect) by bringing stakeholder engagement to a new height and placing it at the heart of the policy formulation process.
The PIL-Approach in Contracts2.0
The PIL approach is also used in Contracts 2.0, an EU-funded project that aims to inform and improve policymaking with regards to the increased provision of environmental public goodsPublic goods are non-rival (they cannot be exhausted) and non-excludable (there are no boundaries). An environmental example in the Contracts2.0 context is an open and beautiful landscape which can be enjoyed by one person without... More in agriculture. In nine European countries (Hungary, Germany, France, Italy, Spain, Belgium, Netherlands, Denmark and United Kingdom) Contracts2.0 established Contracta formal, written agreement for a specified duration signed by (at least) two parties. In Contracts2.0, we acknowledge the existence of informal contracts but use formal contracts to focus the research. More Innovation Labs (CILs), in order to co-design innovative contracts with regional farmers and other stakeholders. The resulting output of the CILs (“dream contracts”) is then fed into the Policy Innovation Labs (PILs). The PIls aim to facilitate the implementation of the novel approaches into the policy framework. They do so by taking a constant feedback from relevant stakeholders (e.g. regional/national policymakers, practitioners and public administrators, scientists, NGOs and associations) into account, to ensure that potential pitfalls are avoided.
The outlined mechanism of interactions within and between CILs and PILs represents an effective bottom-up approach to policymaking by placing stakeholder contributions at the most important stages of the policy cycle (e.g. agenda setting, policy formulation). The multi-stakeholder approach ensures that the different points of view are taking into account. The project framework envisages that the policy requirements formulated in the CILs and refined into policy recommendations by the PILs would be taken up or in some way implemented by policymakers, thus completing the policy cycle (from formulation to effectuation).
How to ensure success?
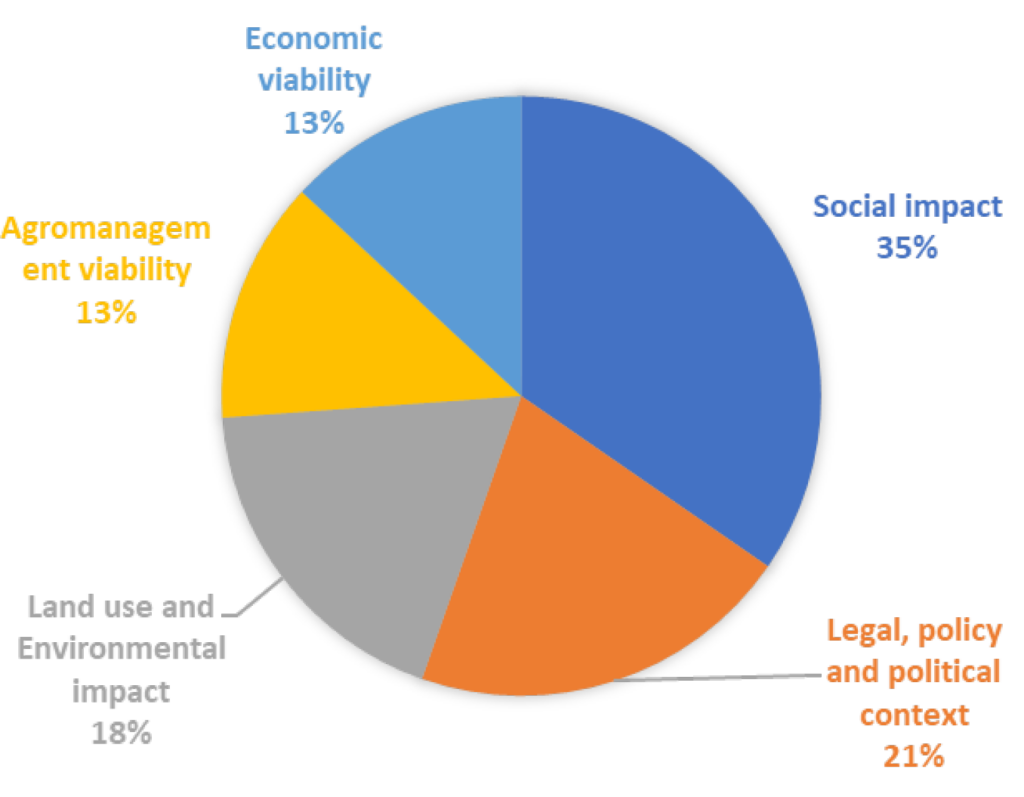
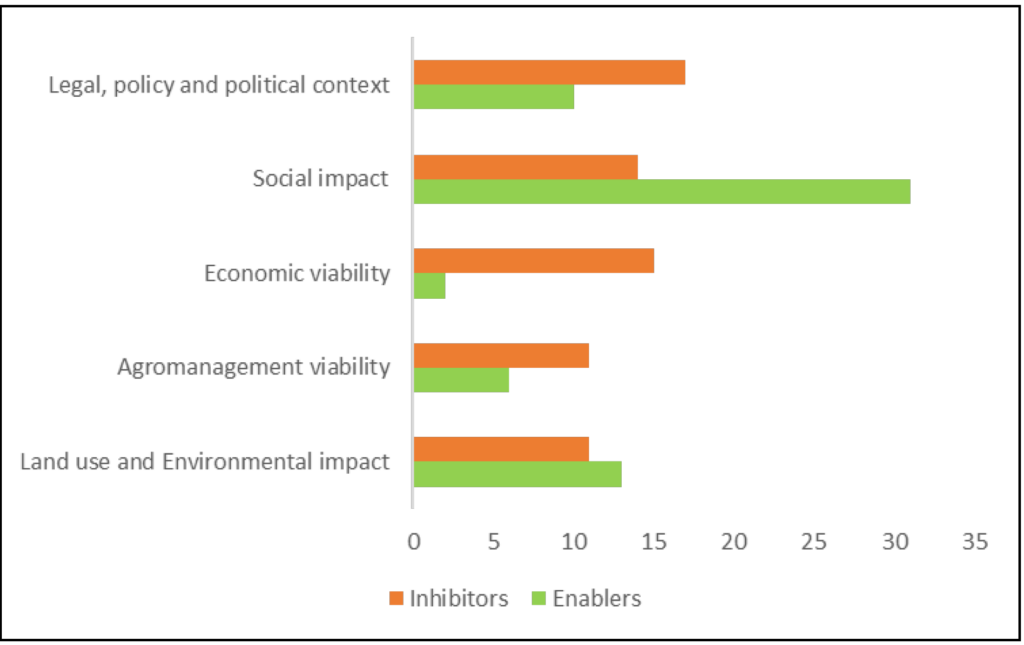
However, the mid-term evaluation of the Contracts 2.0 project and its PIL-approach identified some weak spots, which could prevent the PILs from exploiting their full potential. Some of the assessed PILs report problems regarding an active and consistent pattern of participation of relevant stakeholders in the PIL Workshops. Another risk to the success of the PILs is the potential intertia of administrative institutions and the clinging to the status quo. Features which stand in the way of a recognition let alone adoption of novel policies or recommendations.
While the PIL method is indeed well-designed and has the potential to generate great policy insights, it is important to motivate policymakers to commit to a more consistent support of the co-designing and the implementation of innovative policies. The success of this approach also depends very much on the personality of the involved stakeholders and policy makers, to go out of their way and try something new. The lab coordinators need to address this issue via a tailor-made flow of information and a well-structured discussion culture to facilitate the implementation.
A very important aspect of the PIL-approach in Contracts2.0 is the Cross-PIL-collaboration and integration of research (from the scientific work packages), which enables the exchange of experiences and knowledge across borders, setting off synergies and avoiding duplication of effort. This approach needs to be strengthened in the near future to help inform not only national policymaking but also support the development of a set of more holistic recommendations (e.g. #CAP-Refom) for the development of a conducive common framework while allowing enough flexibility for the individual Member states.
Perhaps in the future governments will rely more on this method of policy innovation, and establish their own autonomous Policy Labs (e.g. similar to that established in Northern Ireland). This way, the bottom-up approach would make its way to the top of national policy-making.
(Written by our guest authors: Ifrah Hassan & Daniel Borsos (School of Public Policy, Central European University)
Further Reading:
Experimentation: https://www.centreforpublicimpact.org/assets/documents/CPI-A-brief-intoduction-to-Policy-experimentation.pdf
Behavioural Insights: https://oecd-opsi.org/guide/behavioural-insights/
Northern Ireland’s government-backed Innovation lab: https://www.finance-ni.gov.uk/articles/evaluation-innovation-lab